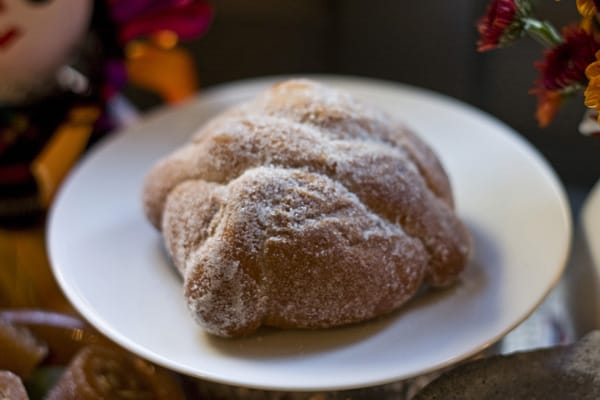
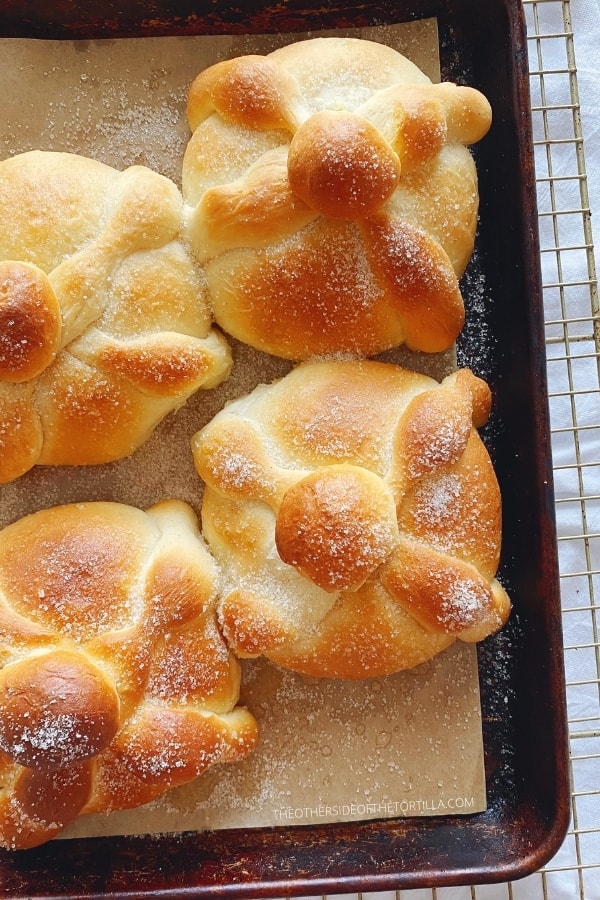
Pan de muerto is a yeasted sweet bread perfumed with orange blossom water or orange zest and dusted with a sugar topping. This pan dulce is typically eaten to celebrate Day of the Dead and is also given as an offering on altars for Día de los Muertos.

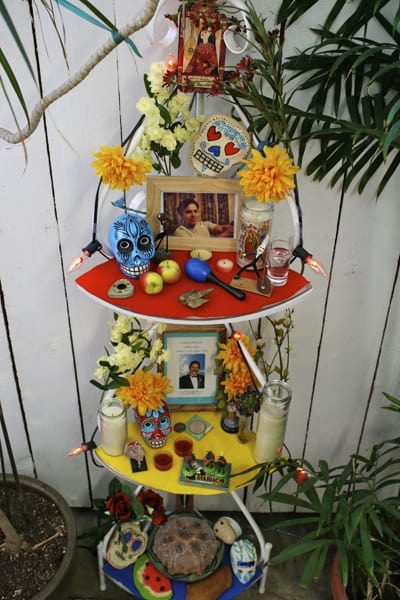
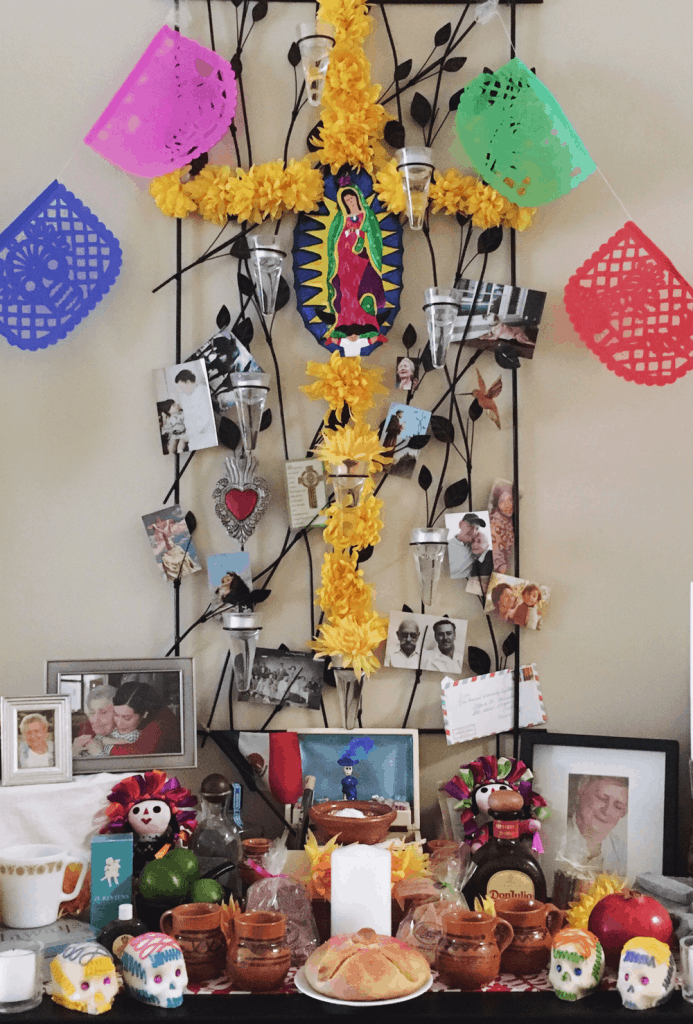
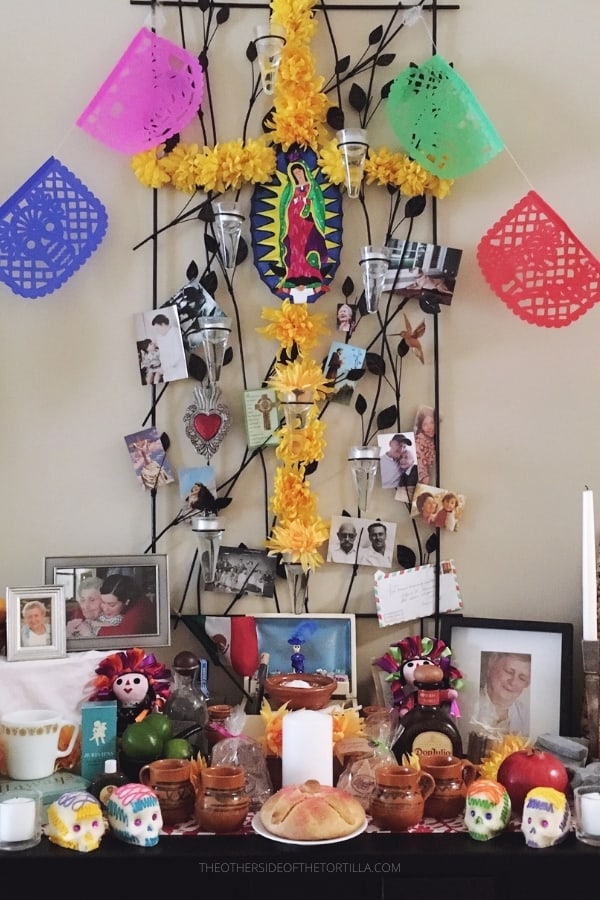
In fact, the most common offering on an altar for Día de los Muertos, aka Day of the Dead, is pan de muerto (literally: “bread of the dead”). Alongside other items included in the ofrenda, the bread is intended to honor the souls of our loved ones who return to visit us and give them nourishment. Other items on the altar may include food and drinks loved by the deceased, trinkets and other symbolic offerings such as marigold flowers (known in Spanish as cempazuchitl), sugar skulls, papel picado, candles and more. You can read more about the symbolic elements of the altar in my post about How to Celebrate Day of The Dead. This holiday is celebrated on November 2, known to Catholics as All Souls’ Day.

Pan de muerto represents an earthly gift and the generosity of the host. The bread dough contains orange blossom water and is often topped with sugar or sesame seeds, depending on the region of Mexico. The dough decorating the top represents bones.
Depending on the region of Mexico you visit this time of year, you may notice that there are other forms this bread can take such as little people, dolls or half-moons. The traditional shape is round with the dough arranged on the top to represent bones. The dough ingredients may also vary slightly according to region, sometimes containing anise seeds or orange zest. In Mexico City, the sugar topping is the most popular. Some areas of Mexico use pink or red sugar, but the most common is plain, uncolored sugar.
In the past, it was common for pan de muerto to be sold in panaderías only a few days prior to Día de los Muertos, but with the growing interest in the holiday outside of Mexico and modern supply and demand marketing, you’re likely to see pan de muerto in grocery stores and some bakeries in Mexico City as early as late August and early September. Even for those who don’t actually celebrate the holiday, it’s common to buy pan de muerto to consume this time of year.
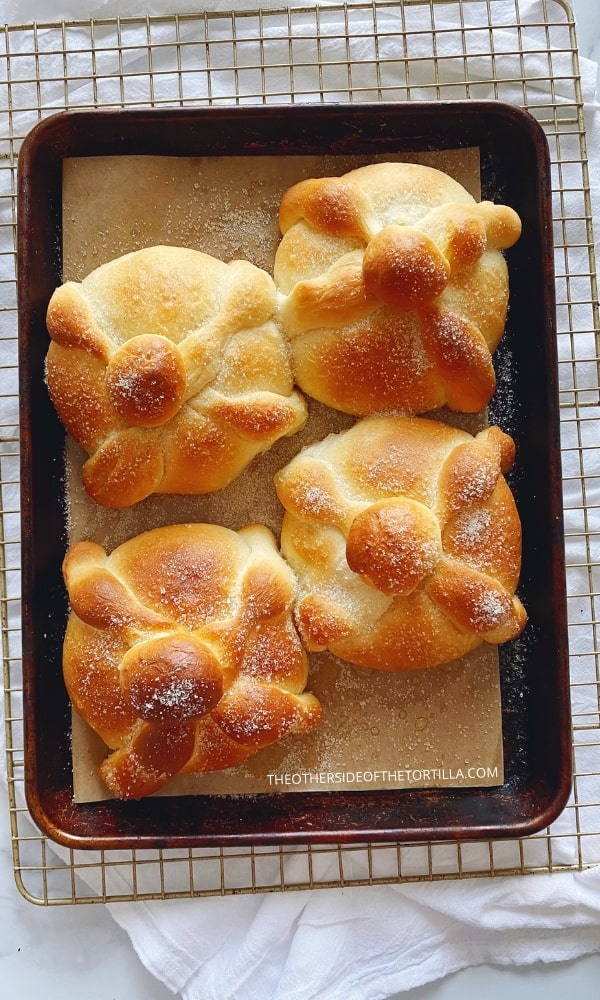

The pan de muerto form you see pictured here is the most common you’ll find in Mexico City; the round base represents a grave mound covering the coffin, the dough shaped like bones represents the arms and legs, and the ball of dough on top represents the skull. The bread itself is made from the same masa bizcocho dough that is used to make conchas, roles de canela, pan de anís, novias, chilindrinas, rebanadas and other similar types of Mexican pan dulce.
You might also like: A-Z Guide to Mexican Pan Dulce
In Oaxaca, the base of pan de muerto is made with their traditional pan de yema, and is sometimes adorned with sesame seeds. In other areas of Mexico, this bread carries other names and has more elaborate decoration as well.
This recipe can make 6 small individual rolls, 4 medium individual rolls, or 2 large pan de muerto breads for sharing with up to 4 people. If you want to make this recipe as one large bread, you may need to adjust the baking time by adding a few minutes.
…